Our Data
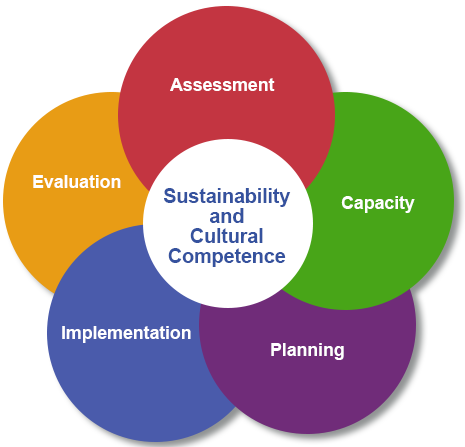
The Strategic Prevention Framework (SPF) outlines a process to prevent and reduce the misuse of alcohol, tobacco, and other drugs. The framework addresses both risk and protective factors. Risk factors are those elements within an individual or the environment that make someone more susceptible to particular negative behaviors or conditions. Protective factors are the opposite – those elements within an individual or the environment that make someone less susceptible to those negative behaviors or conditions. The five steps and two guiding principles of the SPF offer prevention planners a comprehensive approach to understanding and addressing the substance misuse and related behavioral health problems facing their states and communities.
1 . Assessment: Identify local prevention needs based on data.
2 . Capacity: Build local resources and readiness to address prevention needs.
3 . Planning: Find out what works to address prevention needs and how to do it well.
4 . Implementation: Deliver evidence-based programs and practices as intended.
5 . Evaluation: Examine the process and outcomes of programs and practices.
The five steps and two guiding principles of the SPF offer prevention planners a comprehensive approach to understanding and addressing the substance misuse and related behavioral health problems facing their states and communities. The SPF is also guided by two cross-cutting principles that should be integrated into each of the steps that comprise it. The first is cultural competence, the ability of an individual or organization to understand and interact effectively with people who have different values, lifestyles, and traditions based on their distinctive heritage and social relationships. The second guiding principle is sustainability. The process of building an adaptive and effective system that achieves and maintains desired long-term results.
